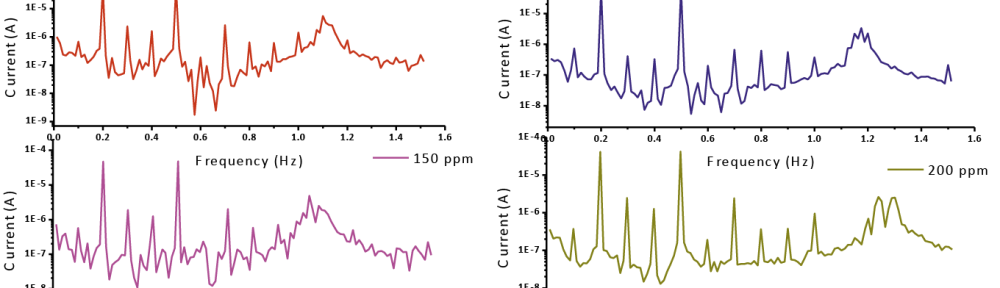Tag Archives: HCl
Malonic Acid as Corrosion Inhibitor for Carbon Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid Solutions
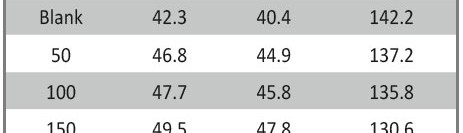
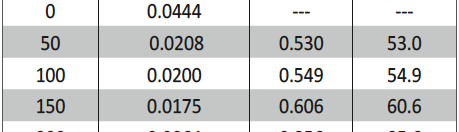
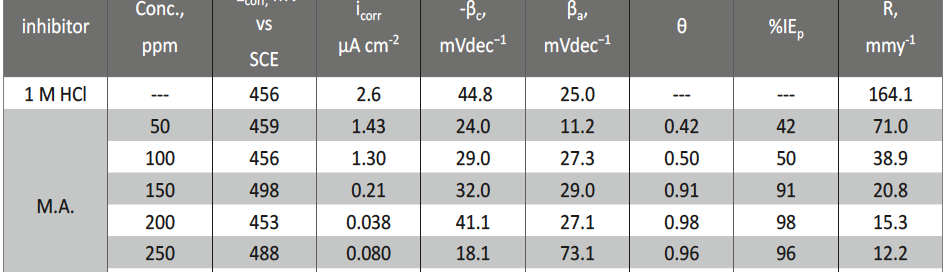
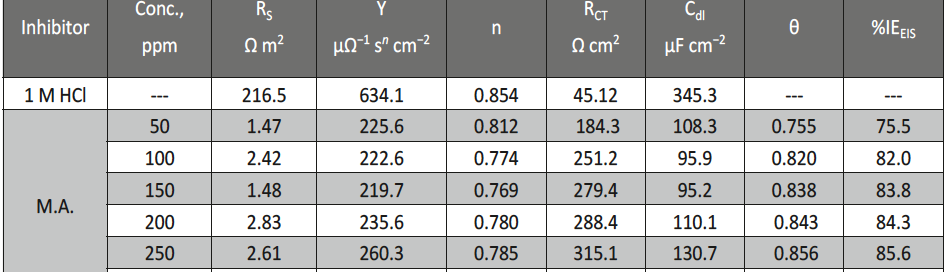
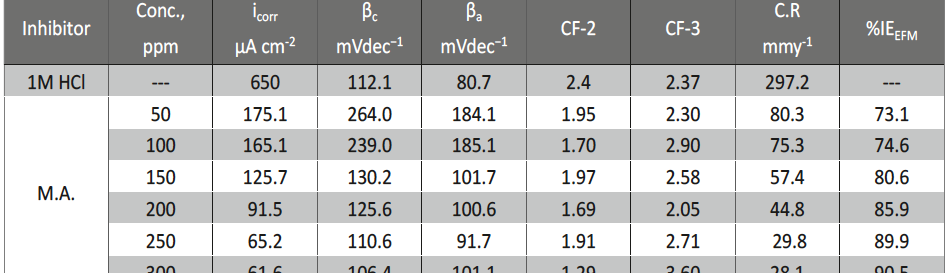
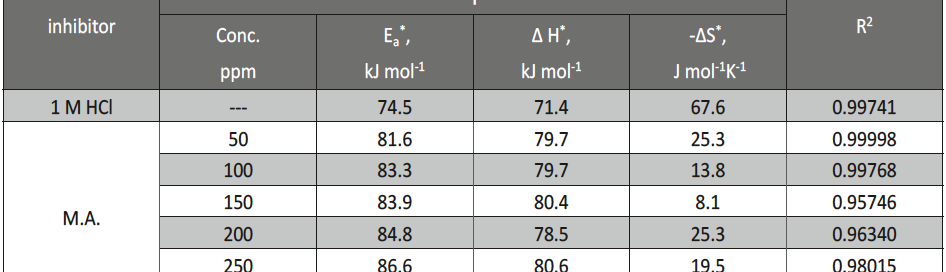
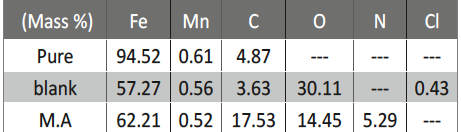
The protection effect of malonic acid on carbon steel corrosion was studied in aerated stagnant 1M HCl solutions at 250C. Measurements were conducted under different experimental conditions using weight loss, Tafel polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical frequency modulation (EFM) techniques. malonic acid was found to be good inhibitor of carbon steel corrosion in1 M HCl. The adsorption of this inhibitor is found to obey the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The calculated activation energies proposed that the inhibitor molecules being physically adsorbed onto the metal surface. Polarization data revealed that this compound behave as mixed type inhibitor.
Adsorption and Corrosion Inhibition Characteristics of Some Thiophene-3-Carbohydrazide Derivatives on Low Carbon Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solutions
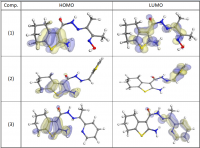
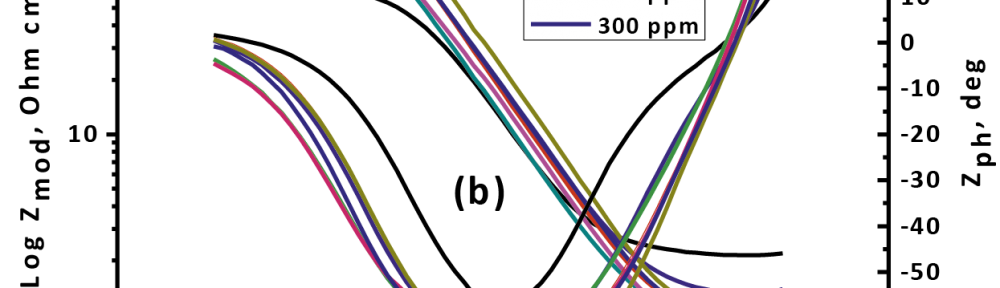
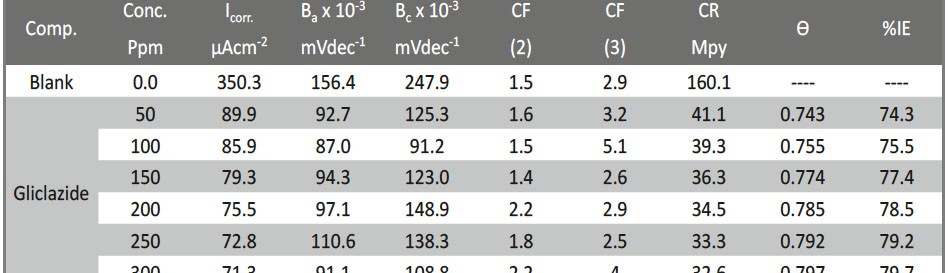
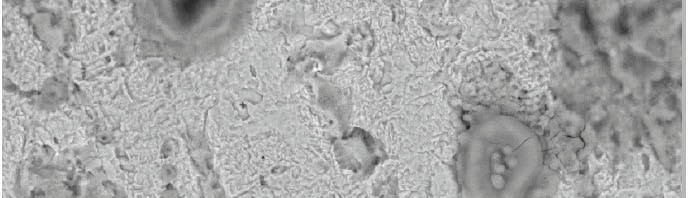
New compounds of corrosion inhibitors namely amino-N’-(3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carbohydrazide (1), amino-N’-(thiophen-2-ylmethylene)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carbohydrazide (2) and amino-N’-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carbohydrazide (3) were synthesized and its inhibiting action on the corrosion of carbon steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid at 25ºC was investigated by various corrosion monitoring techniques. A Potentiodynamic polarization, AC impedance and electrochemical frequency modulation methods have been used. Potentiodynamic polarization studies showed that these derivatives were mixed type inhibitors. The effect of temperature on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in 1 M HCl with the addition of these compounds were studied in the temperatures 25 and 45ºC. The adsorption of these inhibitors on carbon steel surface from hydrochloric acid obeyed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Quantum chemical method is used to explore the relationship between the inhibitors molecular properties and their inhibition efficiency.