Category Archives: General
A Study on Environmentally Friendly Electroless-Plating
Environmentally friendly electrolyte for the electrodeposition of Cu-Zn alloys
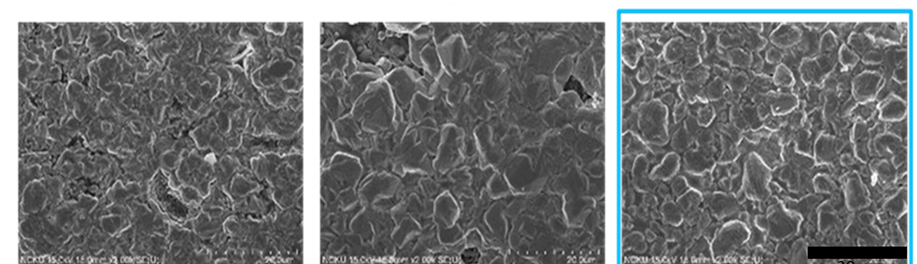
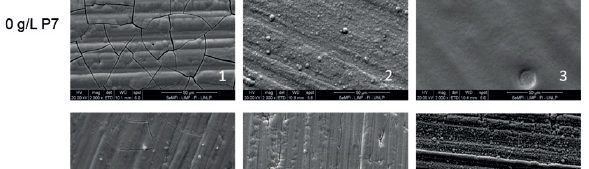
In this work, cathodic polarization experiments on a rotating disk electrode in both static and rotating conditions were carried out using the novel electrolyte with and without the addition of a polymeric cationic surfactant (Polyquaternium-7). The deposits were later dissolved by anodic stripping to characterize the electrochemical processes involved in the Cu-Zn-Glutamate system. Galvanostatic experiments, using flat steel electrodes as substrate, were carried out at different current densities with and without additive. These coatings were characterised by SEM, EDS and XRD.
Cu-Zn alloys with compositions between 37-83 wt.% of copper were obtained. α, β and γ phases were obtained depending on the electrolyte composition and the applied current density.
Investigation of nucleation mechanism and surface morphology of the crystallites in zinc-cobalt alloy coating
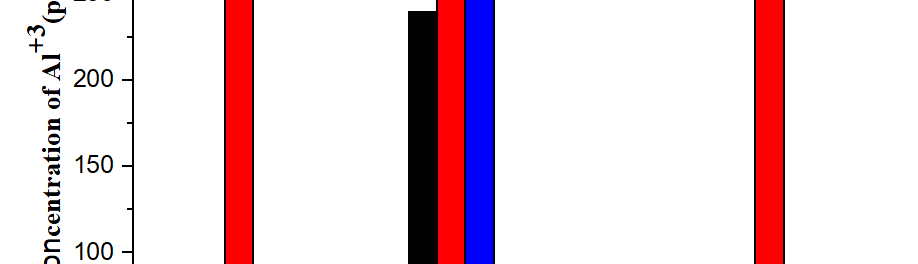
In present investigation, a new brightener was synthesized by condensation of 3, 4, 5-Trimethoxy benzaldehyde and Glycine (TG). Hull cell experiments were conducted to optimize the plating bath components and operating parameters. To examine the influence of TG on nucleation mechanism of Zn-Co alloy electrodeposition, cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry study was carried out. Schariffker and Hills model was used to analyze current transients, which in presence of TG confirmed instantaneous nucleation. Corrosion studies were done using potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopic technique, in 3.5 wt. % NaCl for bright and dull zinc-cobalt alloy coatings. Phase structure, surface morphology and brightness of the deposit were characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscopy and reflectance studies. These studies revealed the role of TG in modifying the nucleation mechanism and surface morphology of zinc-cobalt alloy crystallites and thereby producing a bright corrosion resistant Zn-Co alloy coating on mild steel substrate.
The need for digitalisation in electroplating - How digital approaches can help to optimize the electrodeposition of chromium from trivalent electrolytes
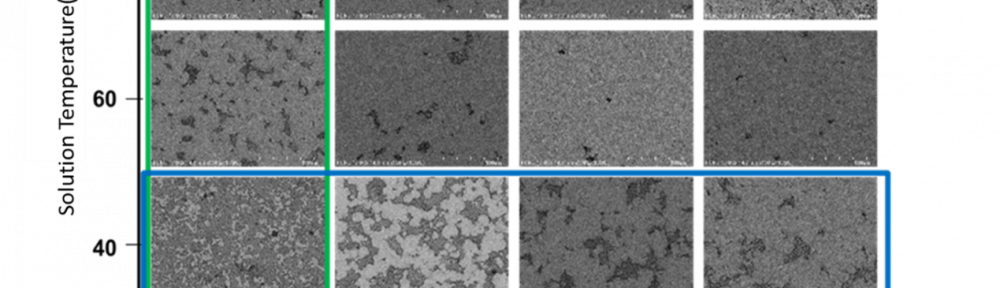
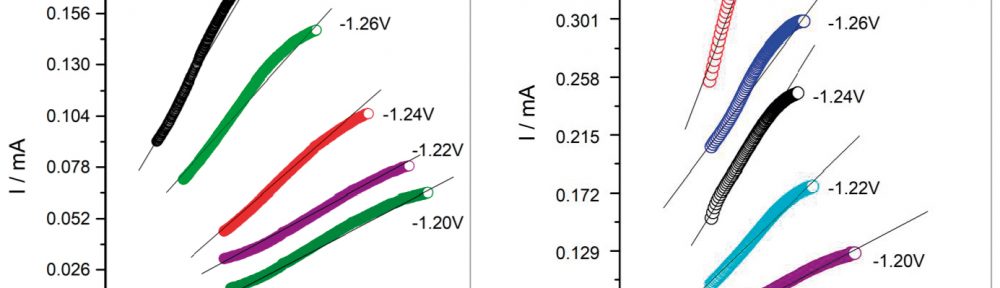
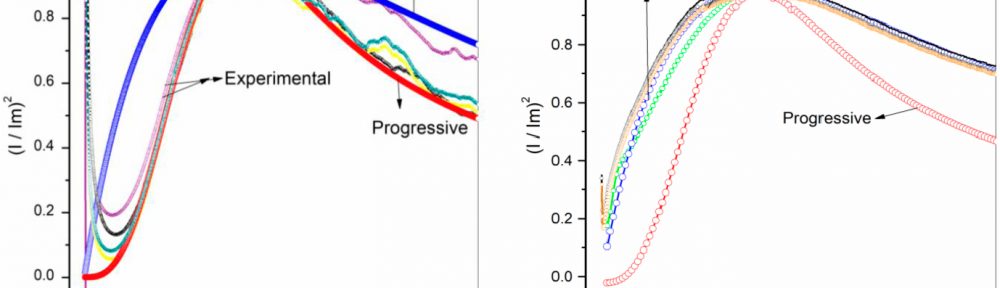
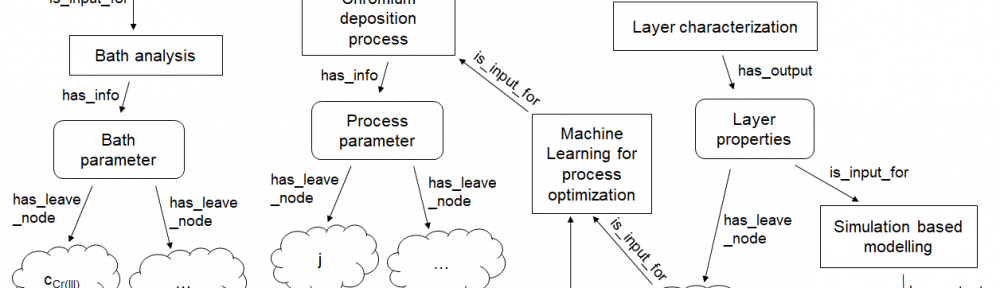
In order to make material design processes more efficient in the future, the underlying multidimensional process parameter spaces must be systematically explored using digitalisation techniques such as machine learning (ML) and digital simulation. In this paper we shortly review essential concepts for the digitalisation of electrodeposition processes with a special focus on chromium plating from trivalent electrolytes.