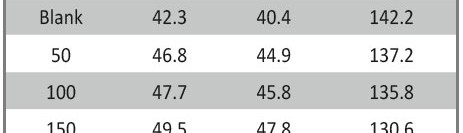
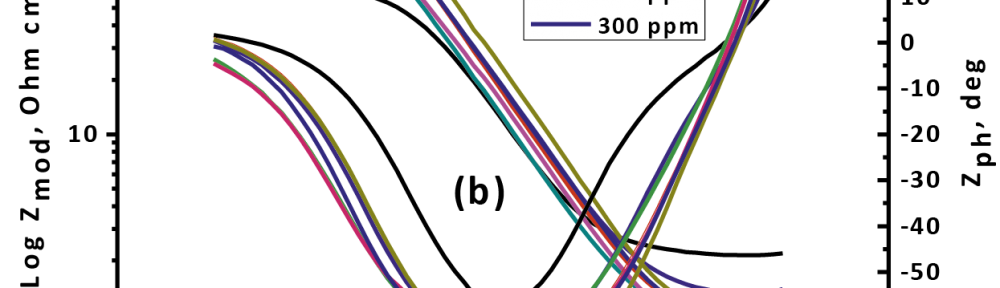
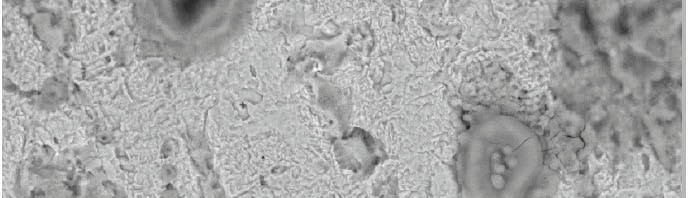
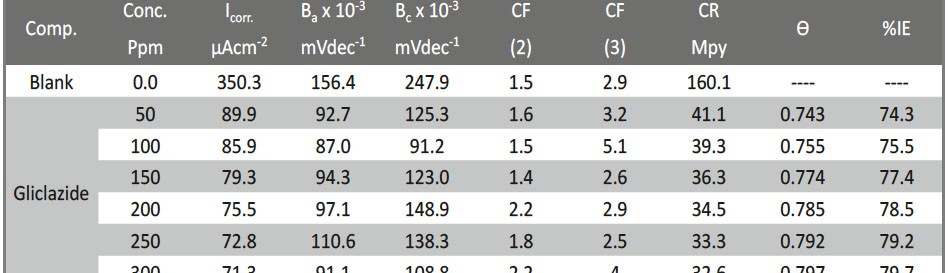
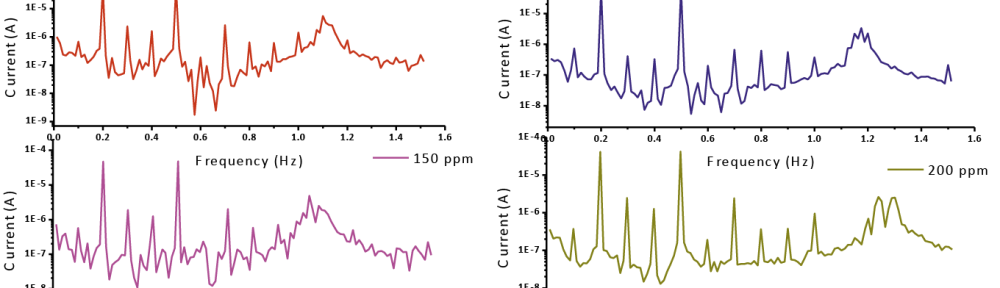The role of Gliclazide as corrosion drugs for CS in 1 M HCl have been studied by using weight loss (WL), Hydrogen evaluation (HE), potentiodynamic polarization (PP), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and Electrochemical frequency modulation (EFM) techniques. Weight loss (WL) studied at various temperatures between (25 – 45oC) but Hydrogen evaluation (HE), Open circuit potential (EOCP) and all electrochemical studied at 25oC and seen that the gliclazide studied are mixed type drug. The effect of temperature on corrosion inhibition, the activation and the thermodynamic of adsorption parameters were determinate. Electrochemical impedance was utilizing to examine the inhibition of corrosion and the mechanism. The existence of the Gliclazide in the solution rise the charge transfer resistance and reducing the capacitance of the double layer. The adsorption of the Gliclazide on the surface of CS was found to obey with Langmuir adsorption isotherm and discussed the thermodynamic parameters (ΔGo, ΔHo and ΔSo) that were determinate. The morphology of inhibition of Gliclazide on CS surface was analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) technology, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), all examine techniques illustrate the formation of thin film from Gliclazide inhibitor adsorbed on the metal surface.It was found the adsorption process is spontaneous and increases, with increasing of inhibition efficiency.