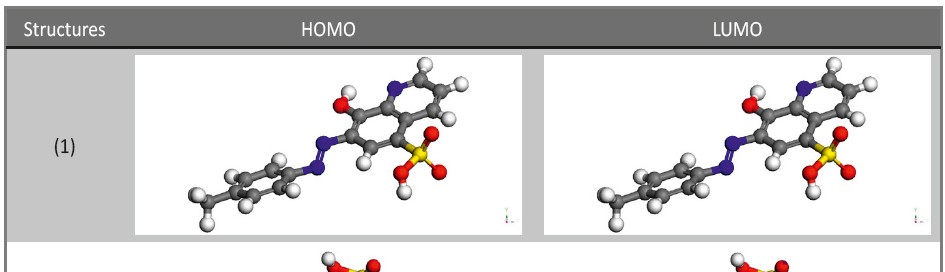
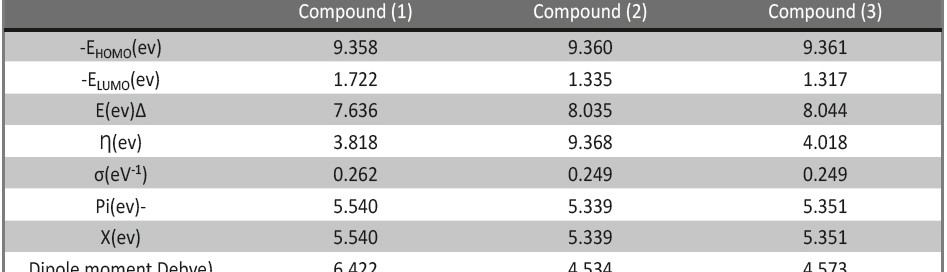
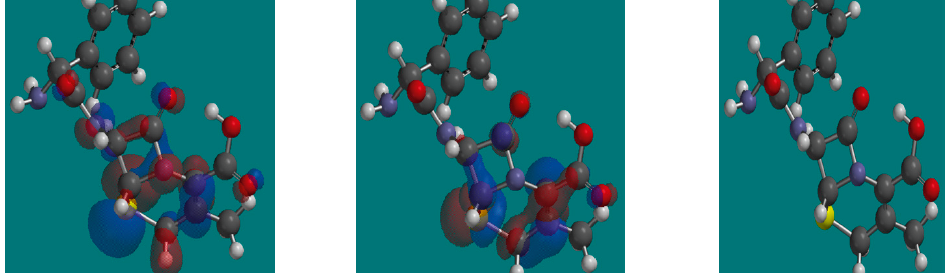
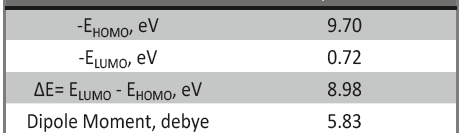
Corrosion Inhibition of copper in nitric acid by 8-hydroxy-7-phenylazo-quinoline-5-sulfonicacid derivatives have been studied using weight loss and electrochemical measurements. The results showed that these derivatives act as moderate corrosion inhibitor for copper at all concentrations of these derivatives. All results indicate that the inhibition efficiency increases with increasing inhibitor concentrations. Polarization curves revealed that these derivatives are mixed type inhibitors. The adsorption of these derivatives on the surface of the copper specimens obeys Temkin adsorption isotherm. Some thermodynamic and kinetic parameters for the corrosion process were calculated and discussed. Some quantum chemical parameters for these derivatives calculated by the density function theory (DFT) semi-empirical method to provide further insight into the mechanism of inhibition of the corrosion process.
Category Archives: General
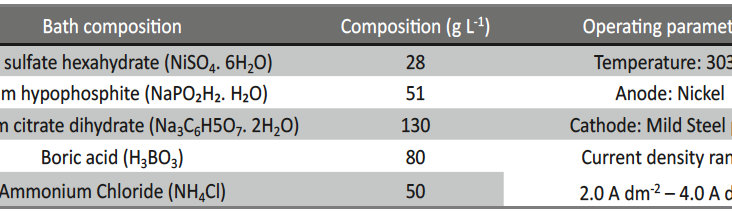
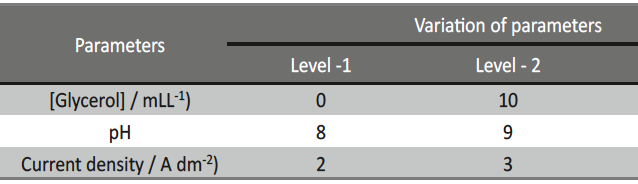
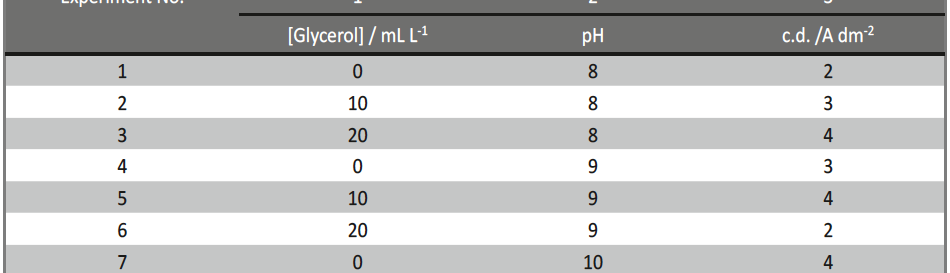
Optimization of Ni-P bath for coatings of maximum hardness and thickness by Taguchi’s statistical approach
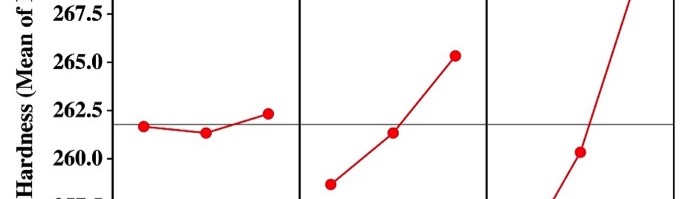
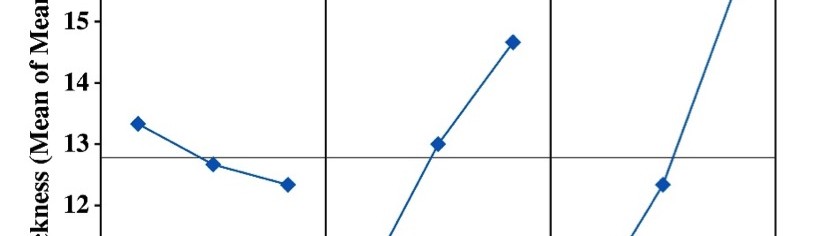
Incredible claims of electroplating in materials synthesis lies in tailoring its property by proper modulation of the bath composition and operating parameters, such as current density (c.d.), pH and temperature. Electroplating of metals/ alloys is one of the most complex process because of the unusually large number of critical elementary phenomena involved during deposition. Due to lack of quantitative guiding principles to develop a coating of desired property, it is very difficult and time consuming to optimize the bath composition. Even though Hull Cell method is an established method to optimize a bath, in terms of its constituents and operating parameters its application is limited to know only the effect of c.d. on deposit patterns; and is incapable for predicting the desired properties of the coating, like hardness, reflectivity, thickness etc. In this direction, this paper describes Taguchi’s statistical method for optimization of deposition conditions of Ni-P alloy, using Minitab 16, Statistical software, by reducing the number of experiments to a practical level. In the present study, bath variables, i.e., [glycerol], c.d. and pH of the bath are taken as chosen parameters and micro-hardness and thickness of the coatings as parameters for characteristic performance. Experimental conditions were optimized to maximize the coating properties. Taguchi’s method demonstrated that the basic Ni-P bath, having [glycerol] = 20 mL L-1, c.d.= 4.0 A dm-2 and pH = 8.0 as ideal for developing coatings of highest micro-hardness and thickness. Experimental data revealed that both [glycerol] and c.d. have close dependency on thickness and micro-hardness of coating, compared to pH of the solution. The experimental steps followed for applying Taguchi’s method, for tailoring the deposit characters are discussed with Tables and Figures.
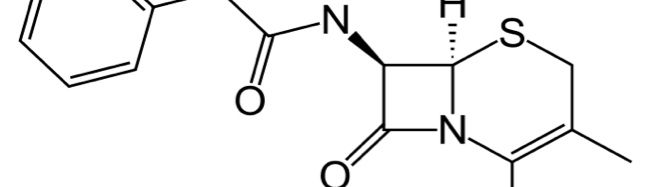
Cephalexin as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Acidic Media Chemical, Electrochemical and Thermodynamic Studies
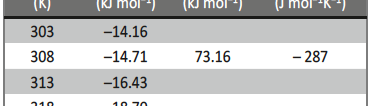
The corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution by pharmaceutical antibacterial drug named Cephalexin has been investigated by using weight loss, potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical frequency modulation technique (EFM) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements. The polarization data showed that this drug is mixed-type inhibitor. The percentage inhibition efficiency was found to increase with increasing the concentration of the drug and with decreasing temperature. The Langmuir`s isotherm was found to provide an accurate description of adsorption behavior of this drug. Some thermodynamic parameters were computed and discussed. The correlations between advanced quantum chemical concepts and inhibition efficiency was found and discussed. The data obtained from different methods are in good agreement.
Corrosion protection of 6061 Al-15 Vol. Pct. SiC(p) composite using a biopolymer- An electrochemical approach
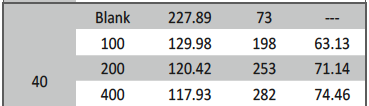
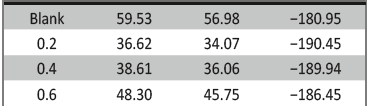
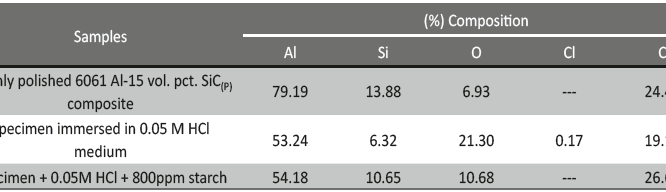
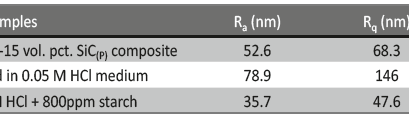
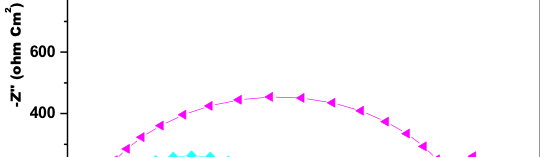
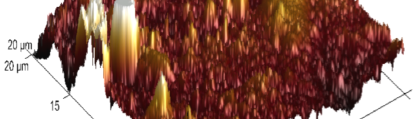
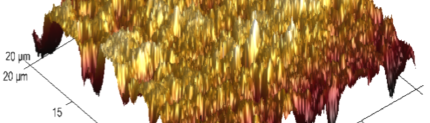
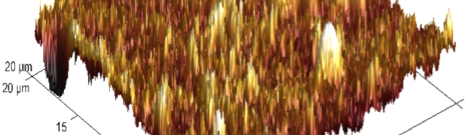
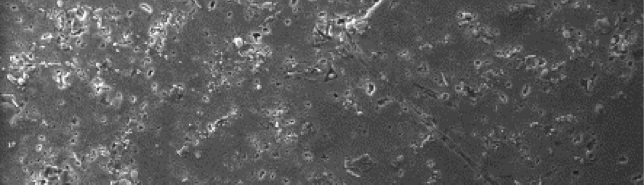
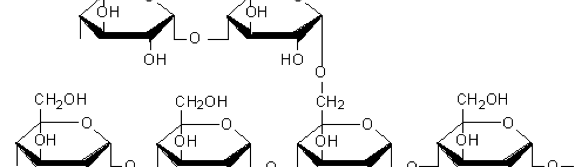
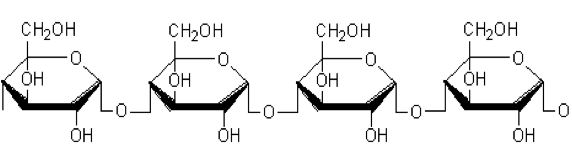
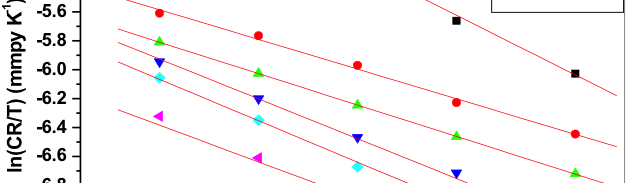
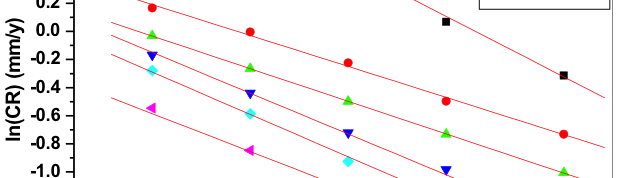
The influence of biopolymer starch as corrosion inhibitor on 6061 Al-15 vol. pct. SiC(p) composite in 0.05M hydrochloric acid was studied by potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique. The surface morphology was studied using SEM, EDX, AFM and XRD techniques. The results showed that the inhibition efficiency of starch increased with increasing inhibitor concentrations and also with increase in temperatures. Starch acted as a mixed inhibitor and underwent chemical adsorption following Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
Malonic Acid as Corrosion Inhibitor for Carbon Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid Solutions
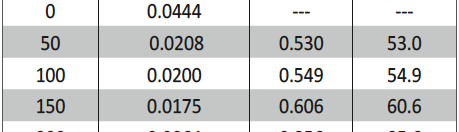
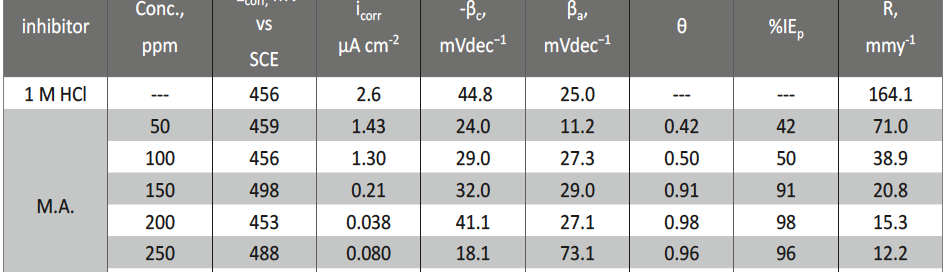
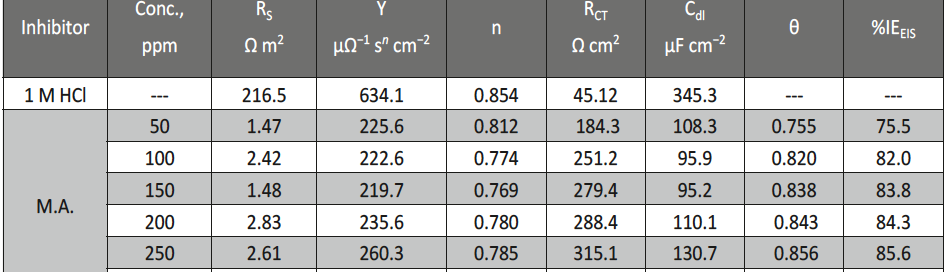
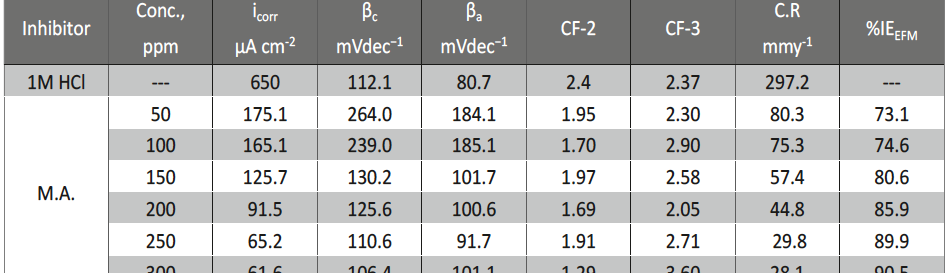
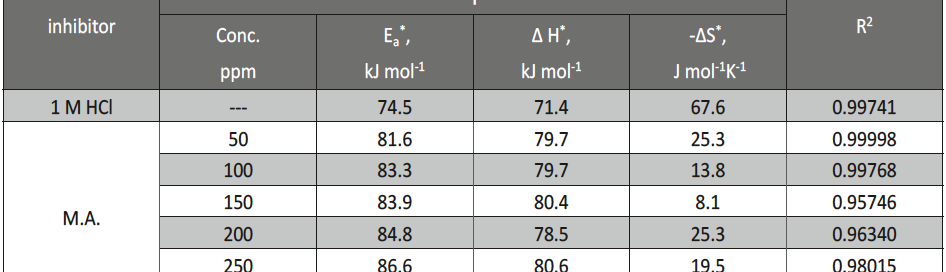
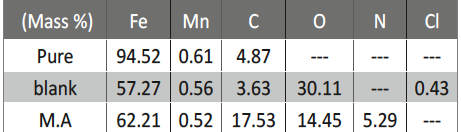
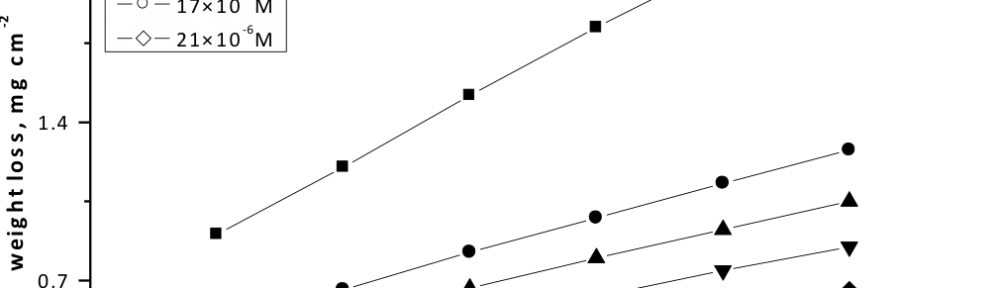
The protection effect of malonic acid on carbon steel corrosion was studied in aerated stagnant 1M HCl solutions at 250C. Measurements were conducted under different experimental conditions using weight loss, Tafel polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and electrochemical frequency modulation (EFM) techniques. malonic acid was found to be good inhibitor of carbon steel corrosion in1 M HCl. The adsorption of this inhibitor is found to obey the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The calculated activation energies proposed that the inhibitor molecules being physically adsorbed onto the metal surface. Polarization data revealed that this compound behave as mixed type inhibitor.


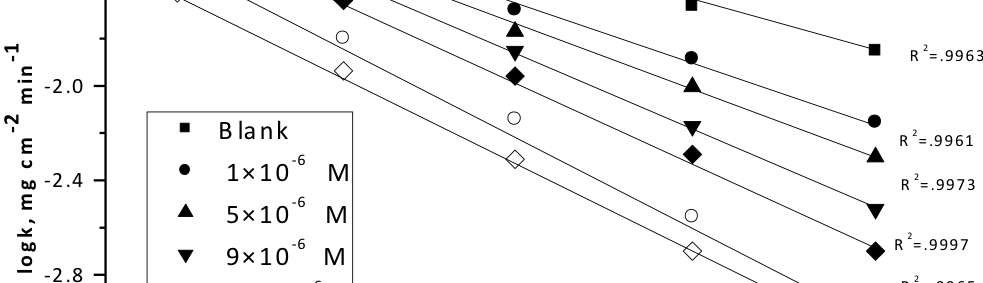


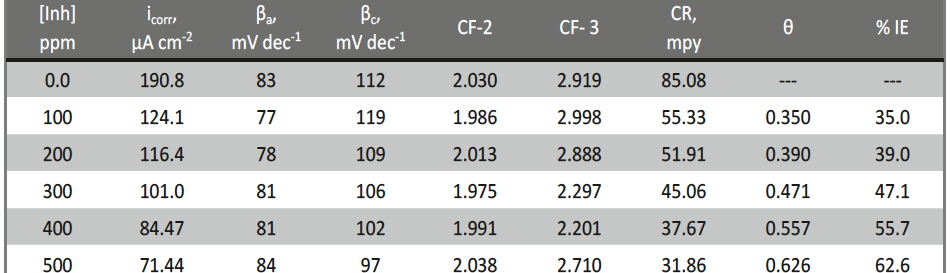
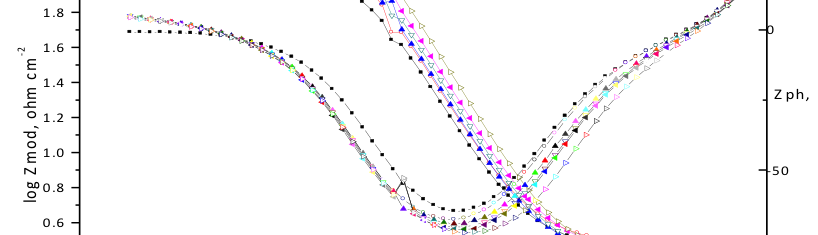
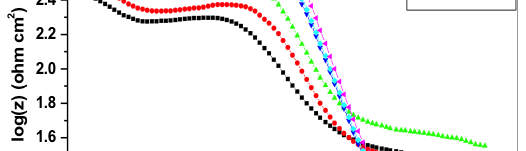
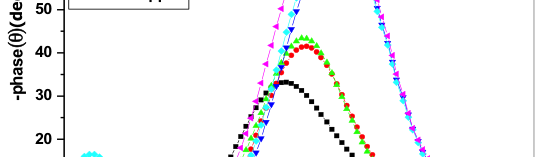
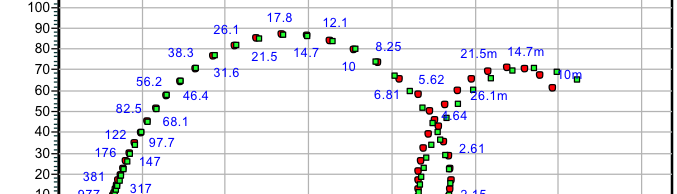
![Fig. 2: Potentiodynamic polarization curves for the corrosion of 6061 Al-15 vol. pct. SiC(P) composite in 0.05M HCl containing various [starch] at 35 °C](https://www.jept.de/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/pic2-578x166.png)
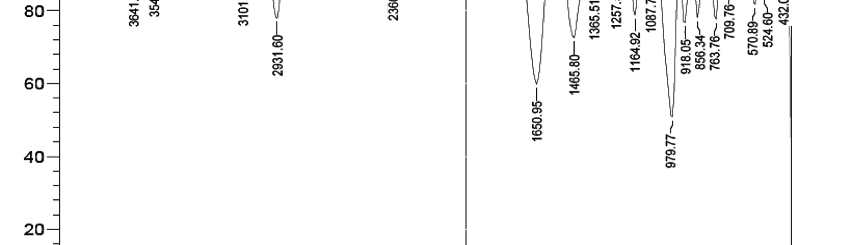




![Tab. 2: Results of Potentiodynamic polarization studies for corrosion of 6061 Al-15 vol. pct. SiC(P) composite in 0.05M HCl containing various [starch]](https://www.jept.de/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/tab2-756x217.png)