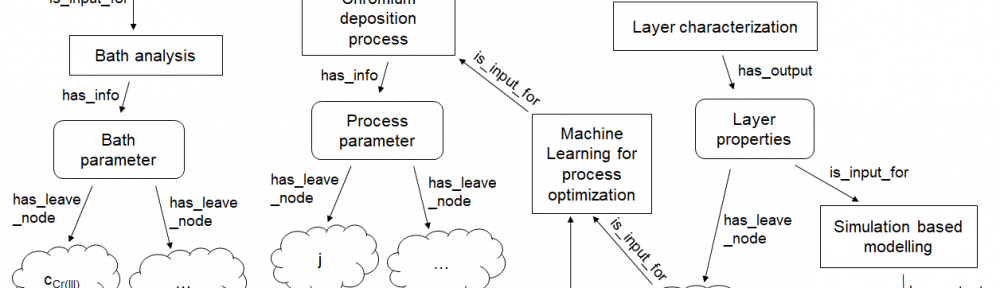
In order to make material design processes more efficient in the future, the underlying multidimensional process parameter spaces must be systematically explored using digitalisation techniques such as machine learning (ML) and digital simulation. In this paper we shortly review essential concepts for the digitalisation of electrodeposition processes with a special focus on chromium plating from trivalent electrolytes.
Author Archives: Dr. rer. nat. Adriana Ispas
Sodium-bismuth-lead low temperature liquid metal battery

The development of a low temperature liquid metal battery based on ionic liquids namely, sodium-bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (Na[TFSI]) in tetraethylammonium-bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide ([TEA][TFSI]) will be discussed. Such a battery should be easily accessible for fluid flow measurements which is still a challenge with the conventional high temperature systems. Cells comprising a Na negative electrode, 20 mole% Na[TFSI] in [TEA][TFSI] ionic liquid electrolyte and a Pb-Bi eutectic positive electrode were constructed and operated at 160 °C. Galvanostatic cycling experiments were conducted at low C rates (C/26) for 13 h corresponding to 50% depth of discharge. A discharge capacity of 565 mAh/g was found. Furthermore electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was used to characterize the aging of the cells.