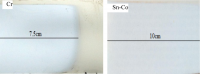
Tin-cobalt alloys were electrodeposited onto nickel-plated brass substrates using a pyrophosphate electrolyte. Deposition conditions were as follows: current density, 0.2-0.3 A/dm2, bath temperature, 45±2°C, pH 8-8.2, ratio of Sn:Co 1.2:1 and current efficiency, approximately 90%. The bath exhibited good throwing power. Deposit morphology was uniform, with cauliflower-like microstructure, mean grain size 125nm. Visual appearance was very similar to electrodeposited chromium with a bluish-white colour. Electrochemical corrosion measurements using Tafel extrapolation and impedance data (as Nyquist plots) showed that Sn-Co alloy and decorative chromium had comparable corrosion resistance with values of 7.77*10-7 A/cm2 and 200 000 Ωcm2 respectively. The results demonstrate that electrodeposited tin-cobalt alloy can be a viable replacement for decorative electroplated chromium.